Defensible Space
A critical factor in determining whether or not a home will survive a wildfire is the type, amount, and maintenance of vegetation surrounding the house. If vegetation is properly modified and maintained, a wildfire can be slowed, the length of flames shortened, and the amount of heat reduced, all of which will assist firefighters in defending a home against an wildfire.
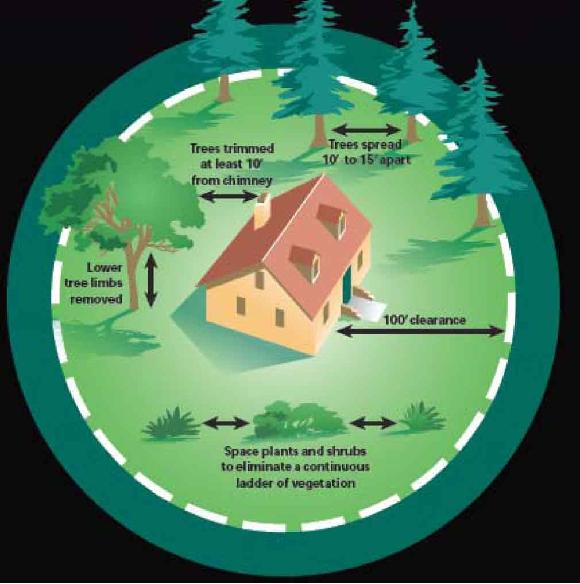
During a major wildfire, it is unlikely there will be enough firefighting resources available to defend every home that is threatened by wildfire, so it is important for homeowners to do their part before a wildfire occurs in order to protect their homes.
To create a defensible space, routine gardening and landscape maintenance practices such as pruning, moving, weeding, plant removal, appropriate plant selection and irrigation are essential. If your home is on flat land, your defensible space distance should extend at least 30 feet from the sides of the house. Make sure the 30-100 feet wide area surrounding the home is LEAN, CLEAN, AND GREEN. The vegetation should be kept:
- Lean- small amounts of flammable vegetation
- Clean-no accumulation of dead vegetation or other flammable debris
- Green-plants that remain healthy and green during the fire season
Tips to Make Your Property Defensible Against Fire:
-Remove dead vegetation (i.e., dead trees and shrubs, dried grass and flowers, dead branches, fallen leaves, etc)
- Remove lower branches from mature trees to height of eight feet from ground level also remove small trees and shrubs growing under mature trees
-Remove tree branches within 15 feet of a chimney or stove pipe.
- Keep vegetation clear of power lines and decks
- Selectively thin and maintain remaining vegetation to 6 inches in height
- Stack firewood and scrap wood piles at least 50 feet from any structure and clear a way vegetation within 10 feet of the piles
- Check and clean your roof and gutters on all structures several times during the spring and fall to remove debris that can easily ignite from a spark

